DBSCAN Extension (Version 0.5) for NetLogo 7 released
A new version of the DBSCAN extension for NetLogo has been released, which makes it compatible with NetLogo 7 (Version 0.4 of the extension has an identical feature set, but targets NetLogo versions 5 and 6 – the description provided below hence equally applies for NetLogo 6). This extension provides modellers with the ability to apply density-based clustering in NetLogo models using the DBSCAN algorithm, which only relies on hyperparameters but otherwise operates unsupervised to derive clusters (unlike K-means, which requires the prior indication of number of expected clusters).
The DBSCAN extension can be added via NetLogo’s Extension Manager and supports the following features:
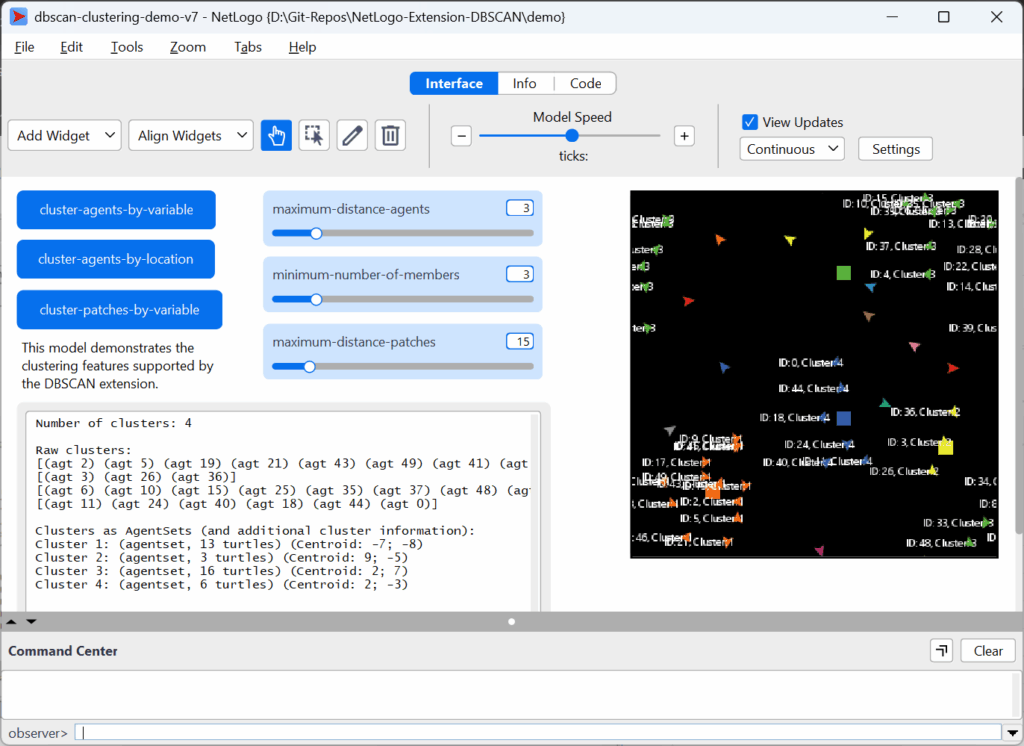
Clustering agents (“turtles”) by location by specifying a maximum permissible distance and a minimum number of agents constituting a cluster.
- Function
cluster-by-locationwith agent set as central argument (click on function name for full syntactic detail) - The following screenshot (of the included demo model) shows this function exemplary:
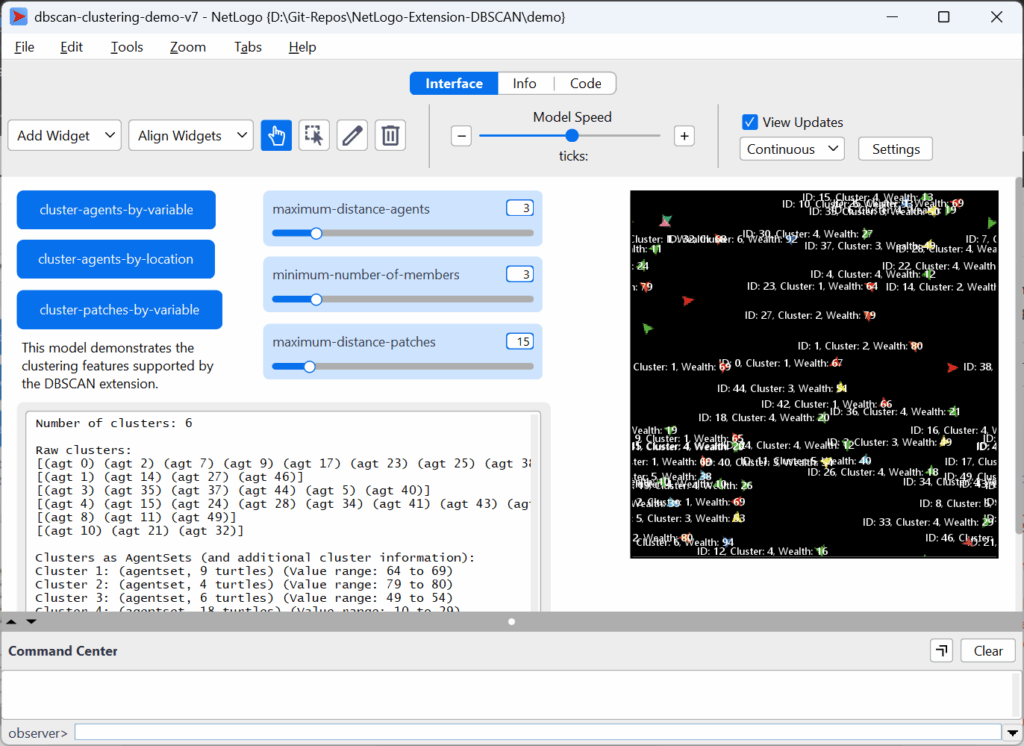
Clustering agents by variable value (e.g., health level, wealth) by specifying maximum permissible value differences and minimum number of agents constituting a cluster.
- Function
cluster-by-variablewith agent set and agent variable/property of interest as central arguments (click on function name for full syntactic detail) - The following screenshot of the attached demo model shows this function exemplary:
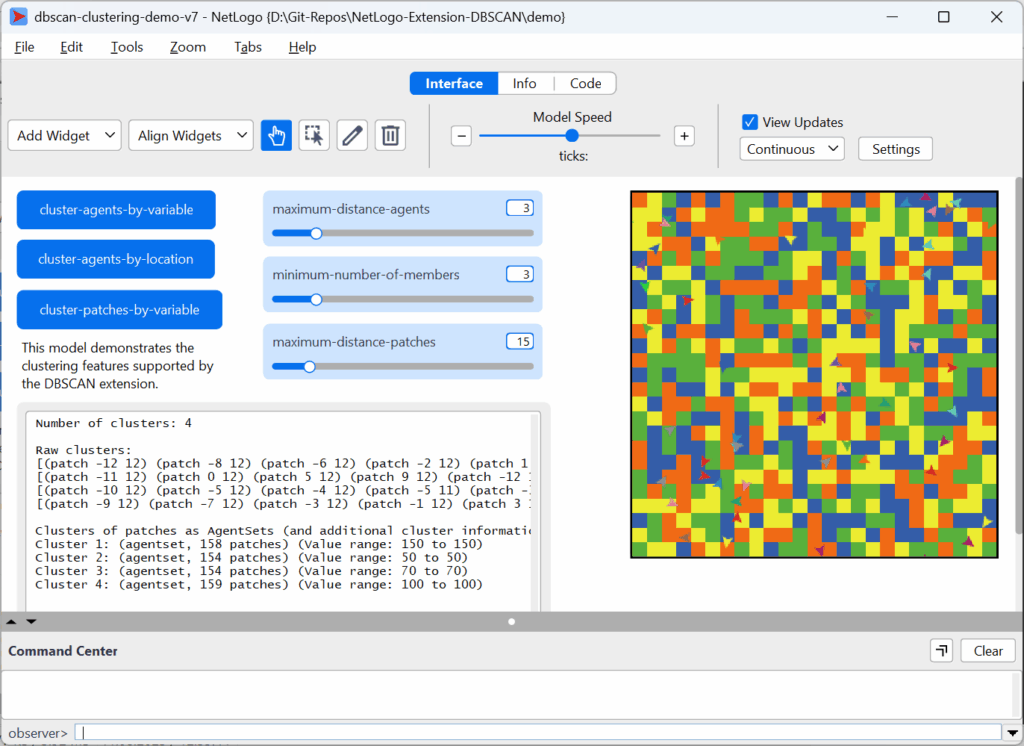
Clustering patches by variable value (e.g., resource level) by specifying maximum permissible value differences and minimum number of patches constituting a cluster.
- Function
cluster-by-variablewith patch set and variable of interest as central arguments (click on function name for full syntactic detail) - The following output shows the application of clustering to patch values:
More details about the full feature set, associated syntax and installation can be found on the extension website: https://github.com/chrfrantz/NetLogo-Extension-DBSCAN#readme (opens in new tab).